Proper and rejuvenating sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health, well-being, and safety. While the general consensus is that most adults need about 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night, individual needs may vary. Some individuals function optimally on 6 hours while others require closer to 10 hours.
While sleep deprivation often takes center stage as a widely recognized issue, oversleeping deserves equal attention due to its potential implications.
Oversleeping, also known as hypersomnia, refers to a condition where individuals experience excessive sleepiness throughout the day, even after obtaining prolonged periods of sleep. It is typically defined as sleeping for 10 or more hours within a 24-hour period.
The causes of oversleeping can range from underlying medical conditions to simply excessive fatigue. However, if left unaddressed, this habit can lead to serious consequences, including chronic diseases, mental health disorders, and cognitive decline.
If you suspect that hypersomnia might be impacting your life, have no worries. We are here to support you by exploring this topic in-depth and equipping you with a wealth of comprehensive information. Throughout this article, we will examine the recommended hours of sleep based on age, shed light on the causes and consequences of oversleeping, and equip you with practical strategies to effectively overcome this issue.
Together, let’s confront this challenge head-on and reclaim mastery over your sleep patterns!
Am I Sleeping Too Much?
The question you must ask yourself first is whether or not you are oversleeping. To guide you in your assessment, the following chart presents the recommendations from the National Sleep Foundation, categorized by age group. It highlights the significance of sleep, as infants and children require more rest for optimal growth and development compared to adults.
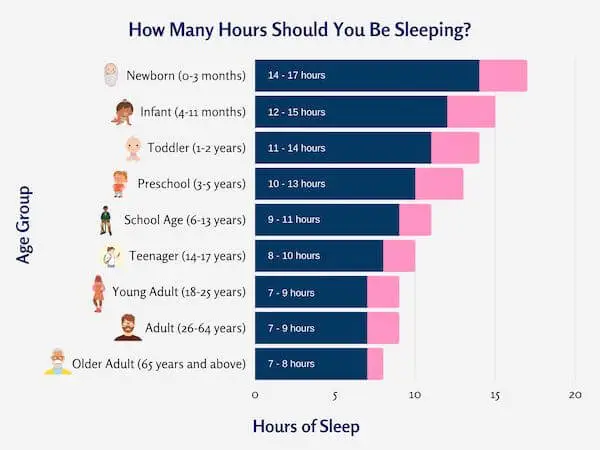
It’s important to recognize that every individual has unique sleep requirements. The recommendations provide general ranges and serve as a helpful guideline. Some individuals may thrive with fewer hours, while others may need to maximize their sleep within the recommended range. Additionally, your specific sleep needs can be influenced by various factors such as pregnancy, medical conditions, and sleep quality.
Personally, I find that I function best with 7 hours of sleep. However, when I exceed my ideal threshold and sleep for 8 hours, I experience negative effects on my cognition and energy levels. Nevertheless, it’s essential to identify the optimal duration that supports your well-being.
Why Am I Oversleeping?
If you suspect that you may be experiencing hypersomnia, it’s crucial to look into the underlying factors contributing to your excessive sleepiness.
Hypersomnia can be triggered by a wide range of events and conditions, encompassing various sleep disorders and medical issues. Let’s explore some of the potential causes.
Sleep Disorders
Conditions such as narcolepsy, obstructive sleep apnea, and restless legs syndrome (RLS) can disrupt your sleep patterns, leading to excessive sleepiness. Narcolepsy may cause sudden, involuntary sleep episodes, while obstructive sleep apnea interrupts breathing during sleep. Restless legs syndrome prompts an uncontrollable urge to move the legs to relieve discomfort.
Idiopathic Hypersomnia
Idiopathic hypersomnia is when individuals experience excessive sleepiness without an identifiable cause.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions like heart disease and hyperthyroidism can contribute to oversleeping. Hyperthyroidism, characterized by excessive thyroid hormone production, can disrupt metabolism and lead to symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and fatigue.
Mental Illnesses
Conditions like depression and anxiety can profoundly impact sleep patterns. Personally, as someone with depression, I understand the challenges of obtaining quality sleep. Depression can manifest as difficulty falling asleep, daytime sleepiness, or oversleeping as a means of escaping from distressing thoughts.
Medications and Substance Abuse
Various medications, including opioids and certain antidepressants, may induce drowsiness and excessive fatigue, potentially leading to oversleeping. I can personally relate to this experience when I was initially diagnosed with depression. One of the antidepressants prescribed to me resulted in sleeping for over 12 hours each night, alongside persistent feelings of sleepiness and drowsiness throughout my waking hours. Substance abuse, such as alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana, can also affect sleep quality and quantity.
Chronic Pain
Patients who experience chronic pain are also very likely to experience hypersomnia due to certain medications or depression.
Your Diet
Your diet plays a big role in your sleep quality. Consuming caffeine late in the day, consuming foods high in sugar or saturated fats, and having a diet low in fiber can disrupt sleep patterns.
Your Environment
External factors such as loud noises and bright lights from outside can disturb your sleep. Similarly, using electronic devices and being exposed to blue light before bedtime can interfere with your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to fall asleep. Additionally, an uncomfortable mattress can contribute to oversleeping.
Why Is Oversleeping Bad?
Oversleeping, when left unaddressed, can have a multitude of effects detrimental to your health.
Common symptoms associated with oversleeping include daytime tiredness, characterized by feelings of grogginess, frequent headaches, and a noticeable decrease in energy levels. Individuals who oversleep often experience excessive daytime sleepiness and a tendency to take frequent naps.
One significant consequence of oversleeping is cognitive decline, leading to difficulties with concentration and memory. It can also exacerbate or contribute to mental illnesses and mood disorders, such as depression. Prolonged episodes of sleep, accompanied by distress, are strongly associated with anxiety and bipolar disorder.
Furthermore, oversleeping is linked to increased inflammation, heightened pain sensitivity (particularly back pain), and decreased immune function. It can also elevate the risk of developing chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and obesity, all of which contribute to a higher mortality rate.
How Do I Overcome Oversleeping?
Now that we have a clear understanding of the causes and consequences of oversleeping, it’s time to regain control of your sleep quality.
Practicing proper sleep hygiene is crucial. For a detailed explanation, you can refer to our previous article on how you can start incorporating healthy sleep hygiene habits.
Here are 10 effective remedies to help you overcome oversleeping.
1. Establish a consistent sleep schedule
Creating a consistent sleep schedule is vital for achieving quality sleep and regulating a healthy sleep-wake cycle. Start by deciding on a time when you will go to sleep and when you will wake up. This will be difficult at first, but over time, your body will adjust to this routine, and you’ll find it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally.
2. Create a calming bedtime routine
Creating a calming bedtime routine can help signal your body and mind that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep. Create a transition period before bed that encompasses calming activities, allowing your body to recognize the shift into relaxation mode. Avoid engaging in stimulating activities close to bedtime, including exercise or taking work calls. Activities that you can incorporate into your bedtime routine to promote relaxation and restfulness include reading a book, taking a warm bath or shower, and listening to guided sleep meditations.

3. Optimize your sleep environment
Transform your bedroom into a haven of relaxation by optimizing its environment to promote restful sleep.
Start by considering the temperature of your sleeping environment. Aim for a room temperature ranging between 60 and 67 degrees Fahrenheit (15 to 19 degrees Celsius). Next, pay attention to the noise level in your bedroom. If you’re sensitive to sounds, consider using earplugs or white noise machines to mask any disruptive noises. Blackout curtains or eye masks can be beneficial in blocking out external light sources and enhancing the darkness in your bedroom.
The importance of a supportive mattress and pillows cannot be overstated, so choose bedding that provides optimal comfort and proper spinal alignment. Having an essential oil diffuser or scented candle can also provide a relaxing mood to help you ease into sleep. Scents that promote relaxation and sleep include lavender, eucalyptus, and chamomile.
4. Unplug from your devices before bedtime
The blue light emitted by phone screens can disrupt your sleep-wake cycle by suppressing the production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep. Engaging in activities like scrolling through social media or watching YouTube before bed not only delays the onset of sleep but also leaves you feeling more fatigued and groggy in the morning. Ideally, keep electronic devices out of your bedroom or at least away from your sleeping area. This allows you to minimize distractions and create a space dedicated solely to relaxation and sleep.
5. Engage in regular physical activity
Regular physical activity plays a vital role in improving sleep quality and promoting better mental health. Exercise triggers the release of endorphins, known as the “feel-good” hormones, which can effectively reduce stress and anxiety levels, leading to improved sleep and an enhanced mood. Exercising in the morning can increase your energy, focus, and productivity for the day while allowing you to feel tired enough by the end of the day to fall asleep more easily. However, it’s important to avoid exercising too close to your bedtime. Late-night workouts can have a stimulating effect on the body and make it harder to wind down for sleep.

6. Be mindful of your diet
What you consume throughout the day can significantly interfere with your ability to have quality, restorative sleep. Consider the following tips:
- Limit caffeine intake, especially in the afternoon and evening, as its effects can linger for several hours. Be mindful of hidden sources of caffeine, such as certain teas, and chocolate.
- Avoid heavy meals and eat dinner earlier to give your body enough time to digest.
- Avoid alcohol consumption before bed, as it reduces the time spent in deep, restorative REM sleep.
- Opt for sleep-promoting foods and beverages, such as foods rich in tryptophan (e.g., turkey, dairy products, nuts), magnesium (e.g., leafy greens, legumes, whole grains), and herbal teas known for their calming properties (e.g., chamomile, valerian root).
7. Harness the power of sunlight
Getting natural light in the morning can significantly influence your sleep patterns by regulating your body’s circadian rhythms. It can enhance alertness and synchronize your internal clock, helping you fall asleep earlier at night. However, if you are exposed to bright light within two hours of your bedtime, it can suppress melatonin production, making it more difficult to fall asleep at your desired time. Whenever possible, incorporate outdoor activities into your daily routine, such as taking a walk during your lunch break or engaging in outdoor exercises.
8. Resist sleeping in on weekends
Resisting the temptation to sleep in on weekends is crucial for maintaining a consistent sleep routine and preserving your body’s natural circadian rhythm. Deviating from your regular sleep schedule can disrupt the quality of your sleep. Personally, I’ve experienced the challenges of sleeping in on weekends, as it throws off my sleep pattern and makes it difficult to readjust on Sunday nights. I find myself struggling to fall asleep at the usual time, leading to grogginess and a lack of energy on Monday mornings. If you’re striving to overcome oversleeping tendencies, it’s advisable to synchronize your sleep patterns. Aim to wake up and go to bed at roughly the same time each day, regardless of whether it’s a weekday or the weekend.
9. Set your alarm and avoid hitting snooze
To conquer the morning alarm battle, a simple yet effective strategy is placing your alarm across the room from your bed. By forcing yourself to physically get up and walk to turn it off, you reduce the likelihood of returning to bed and oversleeping. It takes determination, but resist the urge to hit snooze repeatedly. To make waking up a more enjoyable experience, create a morning routine that excites you. Look forward to starting your day with activities that bring you joy and rejuvenation. For example, savor a freshly brewed cup of coffee paired with a nutritious breakfast, or embark on a peaceful morning walk to witness the breathtaking sunrise.
10. Maintain discipline with your naps
If you need to recharge with a nap during the day, that’s completely fine. Napping within the range of 20 to 30 minutes allows you to obtain the restorative sleep you need while awakening feeling refreshed. During shorter naps, you spend minimal or no time in deep REM sleep. Naps exceeding the 30-minute mark, however, can lead to entering deep sleep, causing sleep inertia upon awakening. Napping late in the day can interfere with your nighttime sleep, so avoid taking naps after 3 pm.

